Fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis are both chronic diseases with no cure. Fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis can both cause some of the same symptoms. They can both take a long time to get the right diagnosis. They’re both more common in women. But fibromyalgia — often called “fibro” — and multiple sclerosis (MS) are two very distinct health conditions with very different causes and treatments, despite having some features in common. Read on to find out the differences and similarities of fibromyalgia vs. MS.
Fibromyalgia and MS may have some more vague symptoms in common, such as problems with focus and concentration, fatigue, and depression. If you’re Googling potential causes of these symptoms, you may find yourself researching both diseases to see if your symptoms match up. But despite some similarities, “for the most part, there is no mistaking symptoms of MS with fibromyalgia,” says Philip Cohen, MD, a rheumatologist, professor of medicine and professor of microbiology and immunology at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University in Philadelphia.
This is especially true once you see a health care provider and start the process of seeking a diagnosis. Fibromyalgia is often diagnosed and managed by a rheumatologist, which is an internal medicine doctor who has specialized training in joint and musculoskeletal diseases. Multiple sclerosis is diagnosed and managed by a neurologist, which is a doctor who specializes in treating disorders of the brain and nervous system.
Read more to learn about the different symptoms of fibromyalgia vs. multiple sclerosis, how fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis are each diagnosed, and how treatments for fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis differ.
The Basics of Fibromyalgia
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that about 4 million American adults have fibromyalgia. While doctors don’t know what causes fibromyalgia, it is a disorder in which people often experience widespread chronic pain and sensitivity to touch, in addition to many other symptoms (more on this below).
“Fibromyalgia is poorly understood,” says Dr. Cohen. “But it’s thought by many to be a disorder of pain perception, perhaps due to abnormalities in parts of the brain.”
Unlike MS, fibromyalgia is not an autoimmune disease, which occurs when then body’s immune system mistakenly attacks your own cells and tissues. Fibromyalgia is not related to inflammation, nor is it a joint or muscle disorder caused by physical injury.
People at higher risk of fibromyalgia include women, the middle-aged, and those with certain diseases, including different types of arthritis, or a family history of fibro. While fibro can impair your quality of life, it doesn’t damage your tissues and organs, or cause medical problems like heart disease and cancer. It is not life-threatening.
Common Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Pain
Though someone with fibro may experience a range of symptoms, the condition’s hallmark symptom is persistent pain in soft tissues and muscles all over the body. “Fibromyalgia pain is diffuse [all over], with particular involvement of what are called ‘tender points,’ or areas of tenderness elicited by pressing in specific parts of the neck, trunk, and extremities,” says Dr. Cohen. Frequently described as a deep ache, the pain may move around, persist for long periods, and disappear.
Fatigue
More than nine in 10 fibromyalgia patients experience unrelenting exhaustion. The sleep problems that often accompany fibro, including light sleep and repeated awakenings, can contribute to fatigue, but treating fatigue in fibromyalgia isn’t just about getting more sleep.
Cognitive issues
People with fibro can have issues with focus, attention, memory and concentration, frequently referred to as “fibro fog.”
Other symptoms
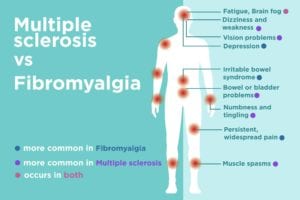
“Fibromyalgia patients often have headaches, irritable bowel symptoms, and depression,” adds Dr. Cohen. “Although these problems may occur in MS, they are less commonly seen.”
The Basics of Multiple Sclerosis
About 1 million Americans are thought to have multiple sclerosis. Unlike fibro, MS is considered an autoimmune disease in which the immune system is attacking part of the central nervous system. Specifically, MS affects the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers throughout your body, which can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on which nerves are affected. Over time, multiple sclerosis can permanently damage your brain and spinal cord.
Doctors don’t know what causes MS but believe that it’s due to a combination of genes and environmental factors. Women, Caucasians, people between the ages of 20 and 50, and those who live farther from the Equator have a higher risk of developing MS.
There are four main kinds of MS; symptoms and disease progression depend on what type you have. While many people with MS develop relatively mild issues (especially with newer treatments that can help prevent MS flares and disease progression), those with severe illness can lose mobility and speech and experience other complications.
Common Symptoms of MS
MS symptoms vary among patients, depending on which parts of the nervous system are affected. The most common type of MS — called relapsing-remitting MS, which is what 85 percent of patients are first diagnosed with — is characterized by attacks, or flares, of new symptoms followed by periods of remission. Among the more common symptoms of MS are:
Muscle issues
Numbness and tingling in the limbs often occur with MS, as do muscle spasms. Frequently, someone with MS will feel an electric impulse sensation when they move their neck a particular way; this is called the Lhermitte sign.
Movement problems
Dizziness and weakness can contribute to balance and coordination troubles. People with MS often complain of feeling suddenly clumsy or report tripping, stumbling, or falling more than usual.
Vision difficulties
When MS affects the optic nerve in your eye, it can cause eye problems such as blurry eyesight, double vision, and vision loss, and may involve eye pain and unexpected movement of the eye. You may find yourself partially color blind and have issues such as picking out clothes that don’t match.
Bladder or bowel problems
People with MS may experience loss of control or other complications with function.
Symptoms That MS and Fibro Have in Common
Though they have few other similarities, MS and fibromyalgia do have some comparable symptoms. These include:
Pain
People with MS may experience eye pain or pain elsewhere in the body. It can be acute or mild, and may be related to neurological issues or musculoskeletal problems. Occasionally, some MS patients do not develop pain. For fibro patients, pain is a defining aspect of the disease. Without its presence, you cannot get a fibromyalgia diagnosis.
Fatigue
Constant weariness is widespread in both MS and fibro. The vast majority of people with either condition often feel physically exhausted, and may find it interrupts their lives at home, school and work.
Cognitive issues
“Fibro fog” is common in fibromyalgia. About half of MS patients report brain fog-like symptoms as well.
When considering your symptoms, it is important to keep in mind that people with multiple sclerosis may experience a wide variety of other issues not common to people with fibromyalgia, such as mobility problems and speech troubles. What’s more, many unusual symptoms may be caused by a condition unrelated to either disease. As a result, it’s crucial to get an an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing Fibromyalgia vs. Multiple Sclerosis
If you suspect you might have either fibromyalgia or MS, says Dr. Cohen, “begin with [your] internist or general practitioner.” They can assess your symptoms and medical history and refer you to the right specialist for further testing.
Both fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis can be difficult to diagnose. There’s no single test that confirms you have either disease, and doctors must rule out other conditions that can have similar symptoms. Read more about diseases that can mimic fibromyalgia.
Diagnosing Fibromyalgia
When diagnosing fibromyalgia vs MS, providers must eliminate the possibility of those other illnesses, which include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, spondyloarthritis, thyroid disorders, and others. To do this, they’ll typically use a combination of patient history, physical exam, and laboratory tests to narrow the field. At the same time, they can look for three diagnostic criteria:
- More than three months of widespread musculoskeletal pain
- Symptoms like fatigue, poor sleep, and cognitive issues
- Where in the body you’ve felt pain over the previous seven days
Read more here about how fibromyalgia is diagnosed.
Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis
Diagnosing MS is different from diagnosing fibromyalgia, since clinicians can rely on certain tests in addition to symptoms, medical history, and a physical exam. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), for example, takes pictures of your brain and helps detect damaged nerves. Other tests may include spinal taps, optical coherence tomography — which scans your eyes for symptoms of MS — and evoked response tests, which look at how your nerves respond to certain stimulation.
According to the National MS Society, an official MS diagnosis requires the following:
- The discovery of damage in two or more separate parts of the central nervous system
- Proof the damage happened at different times
- The ruling out of other diagnoses
Treatment for Fibromyalgia vs. Multiple Sclerosis
While neither illness has a cure, medication can be used to relieve fibromyalgia or MS symptoms. In the case of MS, drugs can also greatly modify the course of the disease. That’s why — though taking medication as prescribed is often key to the treatment of any chronic illness — medication adherence is especially crucial for MS patients.
For fibro patients: Some drugs commonly used to treat depression, called antidepressants, may ease pain and fatigue; these include duloxetine (Cymbalta) and milnacipran (Savella). Anti-seizure medications, frequently prescribed to people with epilepsy, can also help manage pain in fibromyalgia. Among these, the FDA has specifically approved pregabalin (Lyrica) for the treatment of fibro.
For MS patients: There’s been a lot of innovation in recent years to develop different kinds of medications that can help limit damage to the nervous system, reduce relapses, and slow disease progression. These include oral medications as well as medications that are injected or infused. Each medication works differently, but they generally affect immune system activity to prevent it from attacking the nervous system.
People with MS may need additional medication to treat flares, such as corticosteroids, as well as medications to target specific MS symptoms, such as drugs for bladder issues, sexual dysfunction, and muscle stiffness and spasms.
Patients with MS and fibro can also benefit from healthy lifestyle practices, too, including:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help manage symptoms of fibro or mild MS, and may improve mood, fitness and function. Swimming, walking, tai chi, and yoga are smart options. Consult a health care provider or physical therapist about a new exercise regimen, so it can be adapted to individual needs.
- Diet: Though there is no specific diet recommended for MS or fibro, a healthy eating plan may boost your immune system, help manage co-existing conditions, and promote overall good health.
- Sleep: Getting adequate rest is vital for both conditions. It’s recommended that adults between ages 18 and 64 should aim for seven to nine hours nightly.
- Complementary practices: Some patients report that activities like meditation, acupuncture, deep breathing and massage help them relax and ease symptoms.
Keeping a consistent daily routine is often suggested for both fibro and MS, as is leaning on family, friends, and professionals for emotional support. “If there is depression or anxiety, referral to a psychiatrist or counselor is often helpful,” says Dr. Cohen.
While MS and fibro may have some symptoms in common, they are ultimately distinct conditions with very different causes and treatments. Visiting a health care provider can help you get to the bottom of your symptoms quickly and begin the correct therapies. The faster you start, the faster you can start feeling better.