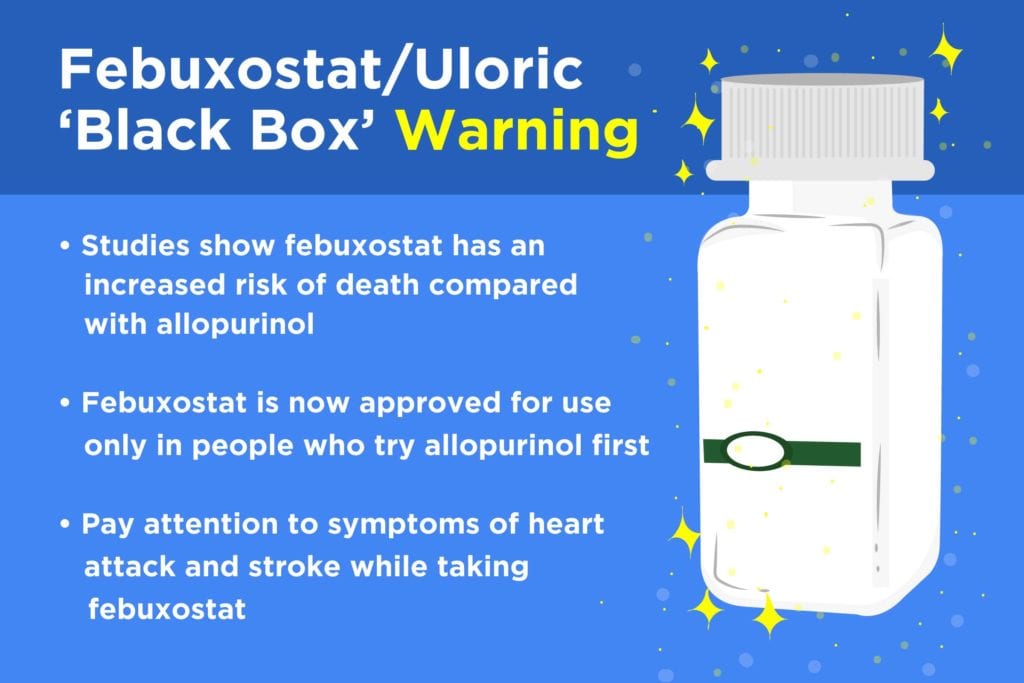

Last month, members of the FDA’s Arthritis Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Committee voted to keep febuxostat (Uloric) on the market as a first-line treatment for gout — despite evidence that users face a higher mortality risk compared to those who take a different gout drug (allopurinol, which is sold under the brand names Zyloprim and Aloprim).
Although the FDA usually follows the advice of its advisory committees, that’s not exactly what happened. The agency has decided that febuxostat is now only approved for use in patients who try allopurinol first.
This ruling isn’t entirely in contrast to what the advisory committees had recommended, since most of the panelists agreed that the majority of gout patients who need a preventive medication for gout should start with allopurinol.
However, the committee members noted that the benefits of febuxostat might outweigh the risks for select patients, including some who might not want to use allopurinol.
Although febuxostat will remain on the market, the FDA has decided that the risks of taking it are great enough to warrant “limiting the approved use of Uloric to certain patients who are not treated effectively or experience severe side effects with allopurinol.”
The FDA is also adding a “boxed warning” (also called a “black box” warning) to the package insert that comes with febuxostat at the pharmacy. This is considered the most severe type of warning the FDA can issue. It’s designed to make sure that users see and understand that a drug could be dangerous — in this case, because febuxostat carries a higher risk for death from cardiovascular disease as well as from any cause (all-cause mortality).
The FDA is urging patients with a history of heart disease or stroke to be extra cautious about using febuxostat. The agency also notes that users should be aware of heart attack and stroke symptoms and get medical attention immediately if any should develop. Those symptoms might include chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, numbness or weakness on one side of the body, dizziness, speech trouble, and a severe headache that strikes suddenly.





